If you’re reading this blog post, it's likely that you're already aware of the versatility of a water jet cutting system in a machining operation. These tools can cut almost any material you or your clients require with unmatched precision and first-cut edge quality. Understanding how the type and quality of your consumables influence cutting costs and component life is crucial for making informed decisions and optimizing your operations.
So, what’s this post about? It's a practical guide to water jet system consumables, providing you with tips on how to reduce your operating expenses and optimize your cutting operations.
Primary Consumables in Water Jet Systems
Every cutting technology relies on consumables to perform its operation. For the sake of this post, we are defining consumables using an Oxford Reference: “materials that are used in a production process that, unlike direct materials, do not form part of the direct cost of sales”. Examples are cooling fluid for production machinery, cutting inserts, and grinding discs.
The major direct consumables for abrasive cutting systems include:
- Water and Water Volume: Water jet cutting, as the name implies, uses high pressure water. The volume of water consumed and its cost varies based on application and geographic location.
- Abrasives: Usually consisting of a garnet material, abrasives are introduced into the high-pressure water stream and provide the cutting media a system relies upon for cutting dense materials.
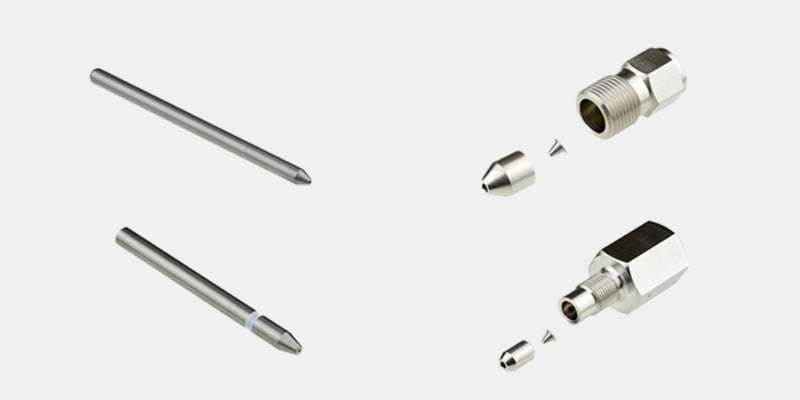
- Abrasive Orifices:
 The orifice reduces the size of the incoming water stream delivered by the high-pressure pump. Orifices are measured by their inner diameter (or ID) and are selected relative to the water flow capacity of the ultra-high-pressure pump. As the water passes through the cutting head body, a vacuum is created in the mixing chamber of the orifice pulling abrasive into the water steam for cutting.
The orifice reduces the size of the incoming water stream delivered by the high-pressure pump. Orifices are measured by their inner diameter (or ID) and are selected relative to the water flow capacity of the ultra-high-pressure pump. As the water passes through the cutting head body, a vacuum is created in the mixing chamber of the orifice pulling abrasive into the water steam for cutting. - Nozzles/Focus Tubes:
 After the orifice reduces the size of the incoming water stream, a nozzle is used to focus the water/abrasive combination and direct it to the cutting surface of the material being cut. Orifices and nozzle inner diameters must be selected in tandem to achieve the optimum garnet flow and water pressure.
After the orifice reduces the size of the incoming water stream, a nozzle is used to focus the water/abrasive combination and direct it to the cutting surface of the material being cut. Orifices and nozzle inner diameters must be selected in tandem to achieve the optimum garnet flow and water pressure.
What Drives Consumable Costs and How Do I Reduce Them?
There are many factors that contribute to the costs of consumables and thus the cost of operating your system. Let's take a look at some of the major ones.
Water supply
In some regions, water supply is taken for granted. In others, not so much. A reliable water supply, as we use it in this context, means having confidence that you will have enough water from your supply source to run your system without interruption. Water use restrictions directly affect the "reliability" of your water supply by imposing usage limits and/or high utility costs from your municipal water utility. Water use restrictions are an increasingly common issue in parts of the United States hit by severe and prolonged droughts.
Open loop systems for process water
Water jet cutting systems require large amounts of water. The volume of water consumed and its cost varies based on application, water source, and geographic location. Most systems rely on a continuous incoming process water stream flowing through the cutting head to make cuts. The continuous water flow feeds into the catch tank and is drained off via an overflow drain. We refer to this as an “open loop system.” Most users simply discharge the excess water directly into the city sewage or drainage system. These open-loop systems incur higher utility costs but avoid the capital cost of water recycling.
Closed loop systems for process water (Jet Edge's recommended best practice)
Closed-loop systems, often referred to as closed loop filtration systems or closed loop water jet recycling systems, reduce total water consumption by recirculating the process water rather than continually discharging it to a drain. Along with an environmental benefit, recycling water is often required by law in areas with water use or wastewater disposal restrictions.
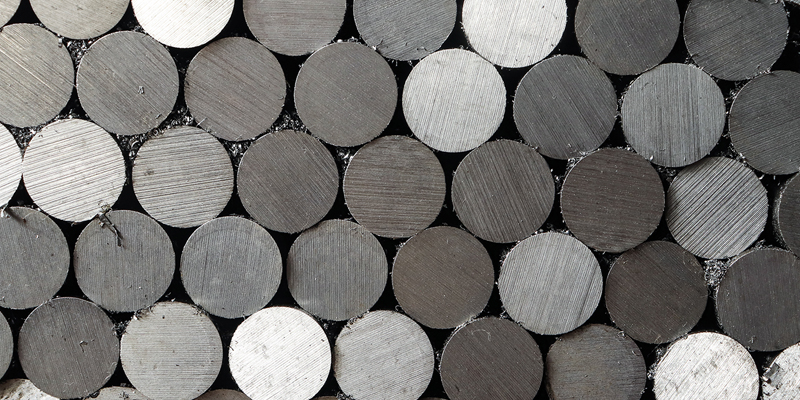
Abrasive selection & flow rates
Garnet is a naturally occurring crystallized aluminum or calcium silicate mineral captured in igneous and metamorphic rocks. As it is mined and collected garnet is crushed into finer grains. The key attributes used to distinguish the different types of garnet are mesh grade, purity, and particle size consistency.
Mesh grade is essentially a size rating of the individual pieces of garnet. The higher the mesh grade, the finer (smaller) the garnet abrasive is and vice versa with 80 mesh being the most common size in water jet cutting. The abrasive orifice and abrasive nozzle ID (inner diameter) size combination will dictate the mesh size limits.
Higher purity and consistent particle size typically means added processing time to sort out non-garnet products and double sifting to ensure more uniform size thus increasing the cost of the garnet. Given the higher price they do deliver superior cutting results and reduce other operating costs created by clogged nozzles and/or removing foreign debris that was left in the garnet during processing.
Best Practice:
We will train your staff to manage all the aspects of keeping your Jet Edge cutting system running smoothly and efficiently. We offer both video-on-demand and live options.
Cutting speed combined with garnet flow rates will determine the cost per inch of a cut. We believe that the best strategy suggests starting with the largest garnet mesh size recommended for a particular nozzle, the highest PSI pump pressure, and then balancing the garnet flow rate with the cut speed to dial in garnet usage that results in the best cutting quality at the optimal cost.
For more information on garnet, check out our blogs: How to Optimize Garnet Use in Water Jet Cutting and Choosing the Right Garnet.
Abrasive orifices
 An abrasive cutting head requires an abrasive orifice to shape the water stream. A natural or synthetic stone is housed in the orifice for this purpose. Sapphire, ruby, and/or synthetic/natural diamonds are the most common materials used in orifices. These materials are able to withstand the rigorous conditions of focusing the ultra-high-water pressure without shattering. However, over time the orifice inner diameter will begin to grow and leak requiring replacement.
An abrasive cutting head requires an abrasive orifice to shape the water stream. A natural or synthetic stone is housed in the orifice for this purpose. Sapphire, ruby, and/or synthetic/natural diamonds are the most common materials used in orifices. These materials are able to withstand the rigorous conditions of focusing the ultra-high-water pressure without shattering. However, over time the orifice inner diameter will begin to grow and leak requiring replacement.
Choosing your orifice by performance:
- Sapphire Orifices – Sapphire orifices have lower hardness making them less expensive but more susceptible to damage than the higher rated tetraCORE and/or diamond orifice shown below. They are more commonly used in less critical applications and/or when users are changing sizes frequently and require a wider range of sizes. Expect a life of up to 80 hours depending upon abrasive application and water quality.
- Ruby Orifices – Ruby orifices provide a smoother, more coherent water stream for a higher cut quality as they are manufactured with a smaller radius on the inner diameter bore. They have lower hardness making them less expensive but more susceptible to damage than the higher rated tetraCORE or diamond orifices. Expect a life of up to 80 hours depending upon application and water quality.
- tetraCORE Orifices – tetraCORE orifices deliver high-quality finishes, fast cut speeds, and last 10 to 15 times longer than the sapphire and ruby orifices. With this extended life you can run longer jobs and will experience less downtime due to fewer orifice change-outs.
- Diamond Orifices – Diamond orifices provide the highest combination of quality, cut speeds and life expectancy. Expect over 1,000 hours of cut life with each diamond orifice as well as an additional 15% longer nozzle life when used in combination. High volume, quality oriented job shops often choose diamond orifices due to the higher quality cuts and less downtime between nozzle changes.
Best Practice:
Saphire and ruby orifices are less expensive and may deliver the cut quality required in many instances. It’s important when comparing the performance of the more affordable orifices with the more expensive tetracore and diamond orifices that you choose the orifice that fits your specific application. Factors and requirements such as quality, speed, and volume all factor into making a smart financial decision. Most OEM’s, including Jet Edge, offer quantity discounting and other incentives to reduce the cost of consumables over the life of your system.
Abrasive nozzles
Abrasive nozzles work in conjunction with the orifice by “focusing” the water/abrasive mix at the cutting surface. If higher-precision cutting is required, a 4-inch nozzle is recommended. As is the case with abrasive orifices, over time, the nozzle inner diameter (ID) will begin to grow creating a wider spray pattern that will impact the finish quality of a part and require replacement.
- Standard Life, Carbide Nozzle - This C4 tungsten carbide nozzle is considered a low-cost, entry level tool. This is the preferred tool for price sensitive shops that use their cutting equipment infrequently or for low volume test cuts. Most production operations will move to a Long or Extended Life for improved accuracy and nozzle cutting life.
- ROCTEC™ 100, Long Life Nozzle - This nozzle is a tungsten carbide-based material made by the patented Rapid Omnidirectional Compaction (ROC) process and is considered by many to be the industry workhorse. Advanced ceramic materials are combined without using a soft metal binder, minimizing the enlargement of ceramic particles. The extra-fine grain size means better nozzle performance and slower wear.
- ROCTEC™ 500, Extended Life Nozzle - Using the Rapid Omnidirectional Compaction (ROC) process, but with even finer grain size and less binder than the ROCTEC™ 100, this nozzle provides higher accuracy and up to 30% longer life than the ROCTEC™ 100, Long Life Nozzle. High performance shops that demand the highest accuracy and cutting life from each nozzle prefer this choice.
Best Practice:
Use your cutting requirements with regards to quality, speed, and volume in order to perform a cost comparison when selecting your nozzle. Most OEM’s, including Jet Edge, offer quantity discounting and other incentives to reduce the cost of consumables throughout the life of your machine.
For more information on choosing the right nozzle orifice combo, check out our blog: How to Choose the Right Nozzle Orifice Combo for Your Water Jet Machine
Extending the Life of Your Components
One of the easiest ways you can extend the life of your consumables is through the use of a short stop filter.
Short stop filter assembly
 Jet Edge offers a short stop filter, an in-line filter that prevents line-borne contaminants from reaching your high-pressure on/off valve needle and seat as well as your orifice. The filter is designed to capture large debris that leads to damage of the needle and seat as well as orifice resulting in premature failure and higher maintenance costs. When the short stop filter is used in conjunction with a diamond orifice, you qualify to be covered by a 600hr orifice guarantee.
Jet Edge offers a short stop filter, an in-line filter that prevents line-borne contaminants from reaching your high-pressure on/off valve needle and seat as well as your orifice. The filter is designed to capture large debris that leads to damage of the needle and seat as well as orifice resulting in premature failure and higher maintenance costs. When the short stop filter is used in conjunction with a diamond orifice, you qualify to be covered by a 600hr orifice guarantee.
Additional cost considerations
Component wear and tear are unavoidable when operating a water jet cutting system. The quality of your consumables directly impacts your first-cut precision and when properly selected, can reduce tool downtime for maintenance and/or parts replacement. Understanding the sources and signs of wear as well as being prepared to address them can help you anticipate and reduce unscheduled downtime. Anticipating and projecting future needs is essential to reducing run costs by taking advantage of bulk purchasing.
Balancing Cut Quality with Consumable Costs
Spending a bit more for quality consumables will reduce your per-part-cutting costs in the long run, and here are a couple of examples:
- OEM parts and seals perform better and last longer.
- Nozzles and orifices made of the most durable materials reduce wear rates.
- Top-quality garnet lasts longer, cuts cleaner, and is ideal for recovery and reuse.
How does paying more for quality consumables reduce costs? Simple, going with quality products results in:
- Less frequent replacement reduces maintenance labor and tool downtime.
- Reusing quality abrasives reduces their costs relative to cheaper single-use alternatives.
- First-cut edge quality remains high, eliminating secondary finishing steps and reducing material scrap rates.
Industry Best Practices
How you use and maintain your water jet cutting tools determines, to a great extent, how well you minimize your consumable costs and maximize component lifespans. Here are five best practices that will go a long way toward helping you balance the (consumables quality + cut quality + component wear) = profit) equation in your favor.
- Regular maintenance and inspections: Follow the recommendations provided by your system’s manufacturer for scheduled maintenance. Enhance their recommendations with a “maintenance-by-walking-around” inspection practice. Before using a water jet tool, have the operator or maintenance crew walk around the tool and its connections, looking for signs of wear and other problems.
- Implement a proper water quality management routine: Your tool’s manufacturer likely has guidelines for optimum water quality parameters. Invest in the best water filters, and regularly test your water quality. Removing sediment and maintaining proper water chemistry can extend the life of pumps, seals, and other components.
- Optimize abrasive use: Use high-quality abrasives, monitor feed rates, and reuse the abrasives when you can take advantage of recycling. and make sure they are properly disposed of. Combined, these actions reduce abrasive consumable costs and help reduce wear on the mixing tubes while maintaining first-cut quality.
- Maintain optimal operating conditions: Make it part of your standard operating procedures to regularly check that your system is cutting at the recommended pressures and within the recommended temperature ranges. Excessive pressure directly impacts the life of seals, tubes, and fittings.
- Operator training: Take pains to ensure every operator understands how to set up, use, and maintain their water jets, including checking for signs of wear. The best practice part here is providing thorough initial training for all operators supplemented by regular refresher training.
Sustainable Cutting Practices
Another way to manage consumable and operational costs while reducing your operation’s environmental impact includes implementing sustainable cutting practices. Here are four practices for your consideration.
Water recycling: Consider investing in a closed-loop water system. These reduce your water consumption, which is an important consideration when you operate in a restricted water use area. It also reduces discharge into streams or rivers (an environmental plus) or your municipal waste system, reducing that cost.
Abrasive recycling: Capturing, cleaning, and reusing your abrasive materials is a terrific sustainability and cost management practice. When you “feed” your abrasive recovery system with high-quality garnet, you can reuse the abrasive many times. Reusing abrasives reduces the amount of material going to a landfill and the associated expense.
Energy efficiency: Where the options exist, invest in high-efficiency pumps and motors. Also, consider implementing a lights-out cutting schedule where you run your system after hours. The cost of electricity is lower, as is the facility's overall energy use.
Reduce material scrap and waste: Nested cutting is a terrific way to maximize stock utilization and is available in advanced cutting software like the IGEMS package we use.
Future Trends and Innovations
Like everything else, technology continues to change in the water jet industry, and some exciting things are in the works. To whet your appetite, here are a few of our favorites:
Abrasives: New materials are under study that will allow faster cutting speeds and longer nozzle life. Eco-friendly options are being looked at, and micro-abrasive machining capabilities are emerging, promising even greater precision, particularly in the electronics and medical device fields.
Reducing component wear: The focus here is on new nozzle materials like carbide and advanced ceramics, while advanced coatings for nozzles and wearing surfaces are being tested to improve component durability.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): You knew AI would be on the list, and it is, with AI tools being developed for predictive maintenance on your equipment and optimizing cutting paths in real-time for maximum material use and providing enhanced cut control.
Industry 4.0 capabilities: This strikes us as AI’s older sibling, where water jet cutting systems integrate with facility-wide Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems and the Internet of Things (IoT). Widely distributed sensors and controls will enable water jets to be monitored, managed, and operated remotely.
Robotics: Let’s see, AI, Industry 4.0 — what’s missing? Robots, of course. Robots have been used industrially for decades. In the cutting industry, robotic arms promise to improve precision further, allowing for the most complex cuts imaginable. They could also enable companies to machine hazardous materials or allow operations in dangerous environments.
Talk to Jet Edge about Consumables and Component Wear
This guide lays the foundation for perfecting the balance between consumable costs and component wear, leading to a more profitable operation. If you have questions about anything we’ve covered or want to learn more about anything water jet systems, get in touch today. Fill out our contact form, or call the US toll-free: 1-800-JET-EDGE (538-3343). International callers can reach us at +1-763-497-8700.

Check Out Our Digital Brochure!
Since 1984, Jet Edge has been designing and manufacturing Ultra-High-Pressure Water jet technology that doesn't back down. Our systems are used around the world in a broad range of industries from the world's leading airlines, to automotive, aerospace and industrial manufacturers, and machine job shops.
To learn more about the Jet Edge difference, our water jet motion systems, pumps and much more, click the button "Download Brochure" to get it now!






%20-%20Jet%20Edge%20Waterjets.png)



